What is amoeba?
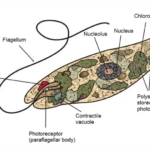
Amoebas (sometimes referred to as Amoeboid) are eukaryotic organisms capable of shape-shifting, with some species being pathogenic. They achieve this shape-shifting movement through extensions called pseudopods. These organisms are often found in freshwater bodies, ponds, and puddles, with some species reaching sizes visible to the naked eye, up to 750 micrometers, while others are as small as 15 micrometers.
One of the most notable species belonging to the genus Chaos, known as the Giant Amoeba or Chaos Carolinense, can grow up to 5 mm in size. As heterotrophs, they can feed on bacteria, algae, other protists, and even small multicellular invertebrates.
Naegleria Fowleri
Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the brain-eating amoeba, is a species of amoeba that, as its name suggests, poses a threat to human health. It is primarily found in freshwater bodies such as lakes, rivers, and hot springs, as well as in soil. Among the Naegleria species, only one is dangerous to human health: Naegleria fowleri.
Occasionally, newspapers report on the brain-eating amoeba. This is due to its high fatality rate, although it claims far fewer lives compared to other diseases and events throughout the year. In the United States, only 148 cases have been reported over 57 years, with only 4 of them surviving. While the sensationalized portrayal in newspapers may cause occasional panic, the risk of contracting it and losing one’s life is minimal compared to other diseases. Nevertheless, caution is advised as there is no effective treatment for the condition it causes.
How is Naegleria Fowleri transmitted?
Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the brain-eating amoeba, is only dangerous when it enters through the nasal passage. If you have been swimming in water containing this species or if water has somehow entered your nose, you are at risk of contracting the disease. In other words, you cannot become ill by ingesting water containing Naegleria fowleri. This amoeba specifically targets the brain through the nasal passage, where it begins to destroy brain tissue. Hence, it is commonly referred to as the brain-eating amoeba and often makes headlines due to its terrifying reputation.
Where is the Brain-Eating Amoeba Found? It can be found in freshwater bodies such as lakes, rivers, geothermal springs, and poorly chlorinated hot tubs. Naegleria fowleri is not found in saltwater bodies like oceans. If pool water is properly chlorinated and treated, you will not contract an infection from it.
How Common is it? In the United States, there were only 37 reported cases over a span of 10 years from 2006 to 2015. Since transmission usually occurs through swimming, infections are most commonly reported during the summer months.
Can it Spread from Person to Person? No, transmission from person to person does not occur. Being in contact with someone who has had the disease does not predispose you to contracting it. As mentioned earlier, transmission occurs when water containing Naegleria fowleri enters the nasal passage and reaches the brain.
This scenario does not occur in chlorinated water sources. For this reason, it is recommended to use distilled or sterilized water that has been boiled for nasal rinsing procedures. Naegleria fowleri can potentially be present in water pipes and drinking sources.
What are the Symptoms of the Brain-Eating Amoeba?
The symptoms of the brain-eating amoeba resemble those of bacterial meningitis. Initial symptoms typically begin within 5 days but can range from 1 to 7 days. These include headache, fever, nausea, or vomiting. Advanced symptoms include stiff neck, confusion, disorientation, loss of balance, seizures, and hallucinations.
Upon onset of symptoms, the disease rapidly progresses and usually results in death within 5 days (ranging from 1 to 12 days). The cause of death is the infection-induced destruction of brain tissue, leading to brain swelling.
The mortality rate is over 97%. Of the 138 cases reported in the United States between 1962 and 2015, only 3 individuals survived. Symptoms of the brain-eating amoeba can also manifest in many other diseases such as meningitis. Therefore, if there is a health concern, it is advisable to seek medical attention without panicking.
Is There an Effective Treatment Method?
It is not fully understood. Several drugs have shown efficacy against Naegleria fowleri under laboratory conditions. However, since most patients succumb to the infection, the results are not conclusive. Recently, two individuals were successfully treated with a new drug called miltefosine (in combination with other drugs).
One of the reasons why an effective method has not yet been found is the rarity of the disease. Although successful experiments have been conducted under laboratory conditions, their effectiveness needs to be tested on humans. However, conducting such experiments and obtaining meaningful results from low case numbers is challenging.
At What Temperatures is it Found?
Naegleria fowleri is a thermophilic organism, thriving in warm temperatures. It grows well up to 46°C and can withstand higher temperatures for short periods.
What Does it Feed On?
It feeds on other organisms such as bacteria living in the sediments at the bottom of rivers and lakes.